
Hip replacement surgery involves changing the damaged surface of the Ball socket type joint and replacing with smooth and durable material.
There has been extensive research in the evolution of Total hip replacement and the technology is still evolving.
Dr Mukherjee performs Hip replacement surgery for –
- Osteoarthritis hip
- Osteonecrosis – Avascular necrosis of femur head (AVN) Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Ankylosing Spondylosis
- Fractures around hip
- Sequelae of Hip dislocation
LONGEVITY OF IMPLANT ?
Various data available is showing up to 92-93% survival of implant at 20 years after surgery. Thus it can be interpreted that it is a lifetime implant if done after 60 years of age. There are 50:50 chance of revision at some point of time if done in young patient. The most common cause of revision is due to implant loosening or periprosthetic fractures due to injury/fall.
There are 2 components in Hip replacement – The Ball ie. The Femur Head And the Socket ie. Acetabulum |
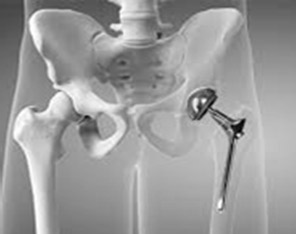 |
Any lower limb surgery which reduces mobility for few days increases the risk of vein thrombosis. We take adequate precaution and prophylaxis for DVT.
Other risk factors include less than 1% risk of infection, change in limb length, risk of fracture while insertion of implant, risk of dislocation of joint, risk of implant loosening, nerve damage to sciatic nerve.
All the complications are treatable, and we advise all patients regarding adequate prevention and management of risk and complications.
What are the options of performing total hip replacement?
First cemented total hip replacement was initially the first choice in 1960s. Both femur stem and acetabulum cup are fixed using cement with the bone.
The cement restrictor is used to block the canal and cement is pressurised using a cement gun. After inserting the implant the position is maintained till the cement gets hardened, thus fixing the implant.
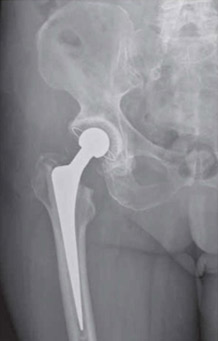
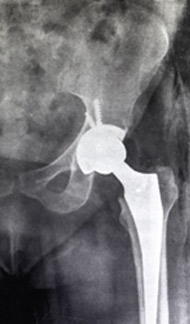
Recent advances
What is DUAL MOBILITY CUP

Improved range of movement with double surface of mobility. Less chance of dislocation.
HIGH POROUS COATED ACETABULUM CUP
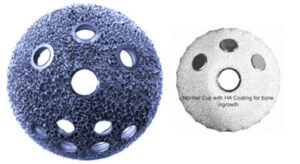
The surface of cup is coated with high porous coating which enhances scratch fit-fixation in bone, better bone ingrowth, less chance of implant loosening.
CONSTRAINED LINER FOR HIP DISLOCATION
A specially made liner to block the femur head within the cup. This is particularly helpful in patients with hip dislocation, old age, paraparesis or weak muscle tone, Parkinson’s disease, post hip fracture.